Z1(ℏω) =
[2 sinh(ℏω/kBT)]-1.
Application of the internal energy formula to the harmonic oscillator
yields
U1(ℏω) = ℏω
( [exp(ℏω/kBT)-1]-1 +½ ) .
The ½ ℏω term is a trivial 0-point contribution which may
be dropped by a suitable re-definition of the 0 of energy.
It is natural to interpret [exp(ℏω/kBT) -1]-1 as the average number of quanta <n> in that oscillator.
U =
∑m ∑ε
U1(ℏω(m))
where the triple summation over m covers the infinitely many wave
vectors k of the oscillators, and the sum over the polarization
vector ε has just two terms (perpendicular to k).
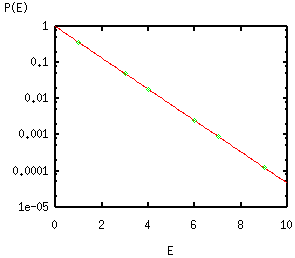
U =
V ∫0∞ u(E,T) dE ,
where
the
energy density per unit volume and per spectral energy interval
u(E,T)
= π-2 ℏ-3 c-3
E3/[exp(E/kBT) -1] .
This integration can be performed analytically, to get the total thermal equilibrium energy density of the electromagnetic fields
U/V =
π2(kBT)4/(15ℏ3c3).
Any surface absorbs a fraction α and re-emits a fraction γ of the radiant energy it receives. Beside depending on the chemical nature of the surface, both these quantities depend on the frequency ω or photon energy E of the radiation (and on the surface temperature). The way these quantities vary with E expresses the surface color. Energy conservation guarantees that α(E,T) + γ(E,T) = 1. Energy balance between a thermal equilibrium radiation in a cavity and the cavity walls at the same temperature requires that the absorbed power fraction (per unit surface) α(E,T)×RB(E,T) be entirely re-emitted by the surface. As a consequence, any surface kept at a given temperature T emits [in addition to the reflected/diffused radiation γ(E,T)×(irradiation received)] extra radiation with an equilibrium spectrum multiplied by the surface spectral absorbance. Consequently, a perfectly "black" surface ( α≡1 through the spectrum) kept at a given temperature must emit the spectrum RB of electromagnetic fields in a cavity to guarantee energy balance. This explains the name blackbody radiation.